二叉树是一种树形结构,其中每个节点最多有两个子节点,通常称为 左子节点 和 右子节点。它的基本性质主要有以下两个方面:
-
每个节点最多有两棵子树,所以二叉树中不存在度大于 2 的节点。
-
子树有左右之分,顺序不能颠倒。
二叉树的类型
二叉树有多种类型,每种类型都有其独特的特性和应用场景。
满二叉树
满二叉树的定义:
-
每个节点要么是叶子节点,要么有两个子节点的二叉树。
-
所有的叶子节点都在同一层上。
性质:
-
如果一棵满二叉树的高度为 h,那么它有 2^h - 1 个节点。
-
每一层的节点数都是最大值,第 i 层有 2^(i-1) 个节点。
它的示例如下:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7完全二叉树
完全二叉树的定义是一棵二叉树,如果除了最后一层外,其它各层的节点数都达到最大,并且最后一层的所有节点(从左到右)连续排列,这样的二叉树称为完全二叉树。
它的性质是节点数为 N 的完全二叉树的高度为 ⌊log2(n)⌋ + 1,在完全二叉树中,节点从上到下,从做到右依次排列,没有空缺。
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ /
4 5 6二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一种二叉树,其中每个节点的左子树中的所有节点的值都小于该节点的值,而右子树中的所有节点的值都大于该节点的值。
二叉搜索树的特点就是中序变量二叉搜索树会得到一个递增的有序序列,无论是查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度平均为 O(log n),最坏为 O(n) 也就是当树退化成链表时。
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ / \
1 3 5 7平衡二叉树(AVL Tree)
平衡二叉树的定义是每个节点的左右子树的高度差之多为 1 的二叉搜索树,平衡因子(Balance Factor)是指某个节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度的值,其取值只能是-1、0、1。
它在保持二叉搜索树的有序性,同时尽量平衡,使得查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度保持在 O(log n)。通过旋转操作(单旋转和双旋转)来维持平衡。
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
1 3 5它的性质是保持二叉搜索树的有序性,同时尽量平衡,使得查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度保持在 O(log n)。它可以通过旋转操作(单旋转和双旋转)来维持平衡。
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
1 3 5二叉堆
叉堆(Binary Heap)是一种特殊的完全二叉树,用于实现优先队列。二叉堆分为两种:最大堆(Max Heap)和最小堆(Min Heap)。在最大堆中,每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值;在最小堆中,每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值。
拿最小堆来举例,它的根节点的值是所有节点中最小的,每个子树也都是最小堆。
二叉堆是一棵完全二叉树,即所有层都是满的,只有最后一层可能不满,但节点尽可能靠左,最小堆中,父节点的值小于或等于其子节点的值。
二叉堆通常使用数组来表示,这样可以避免使用指针操作,提高效率。
-
父节点索引:对于节点索引 i,其父节点的索引为
(i - 1) // 2。 -
左子节点索引:对于节点索引 i,其左子节点的索引为
2 * i + 1。 -
右子节点索引:对于节点索引 i,其右子节点的索引为
2 * i + 2

React 为什么要采用最小堆
在 React 中,借助 Fiber,它可以将任务拆分成多个小任务,每个小人物的数据结构带着一个 expirationTime 的对象,expirationTime 表示这个任务的过期时间,expirationTime 越小就表示过期时间越近,该任务的优先级就越高,取出最小值就相当于取出优先级最高的任务。
最小堆的一个重要性质是能够在 O(1) 时间复杂度内找到最小值,同时在 O(log n) 时间复杂度内插入和删除元素。由于 React 需要频繁地处理高优先级任务(即最小优先级值任务),最小堆能够高效地完成这些操作。
当用户交互产生新任务时,需要调整现有任务的优先级。最小堆可以快速调整任务的顺序,以确保高优先级任务先被处理。
React 的最小堆涉及这 6 个函数:
-
push:往最小堆插入新节点
-
pop:删除根节点,就是那个最小的值
-
siftUp:上浮,不停地交换节点和父节点
-
shiftDown:下沉,不停地交换节点和子节点
-
peek:获取根节点,也就是数组的第一个元素,也就是优先级最高的那个任务
插入
将新节点插入到堆的末尾,然后调用 siftUp 函数来调整堆,保持最小堆性质。
我们尝试在下面这个二叉堆中,插入新节点,它的值为 1,我们会将这个值与父节点的值进行对比,如果小于父节点,就交换两个节点,就这样不断比较上浮,直到父节点比它小。如下图所示:

React 的源码实现如下所示:
type Heap = Array<Node>;
type Node = {|
id: number,
sortIndex: number,
|};
export function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
function siftUp(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
return;
}
}
}
function compare(a, b) {
const diff = a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
return diff !== 0 ? diff : a.id - b.id;
}在上面的代码中,>>> 是无符号右移运算符,这里用于计算父节点的索引。(index - 1) >>> 1 相当于 (index - 1) / 2,用于找到当前节点的父节点索引。
我们来看一下 7>>>1 的例子,如下结果所示:
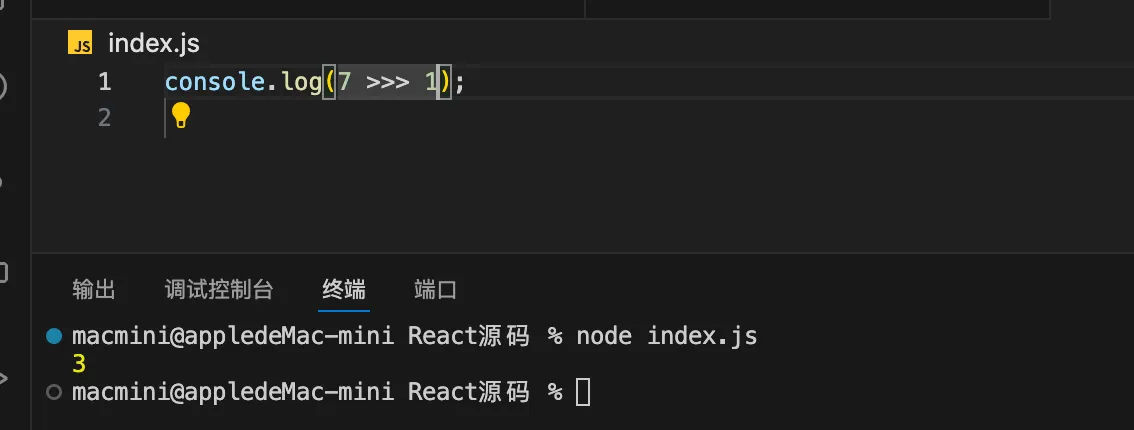
首先将 7 转换为 32 位的二进制数 00000000000000000000000000000111,使用无符号右移操作 >>> 1 将该二进制数向右移动 1 位,右移 1 位后,右边的位会被丢弃,左边用零补齐。
移动后的二进制表示为 00000000000000000000000000000011,转换为十进制数为 3。
如下代码所示:
class HeapNode {
sortIndex: number;
id: number;
constructor(sortIndex: number, id: number) {
this.sortIndex = sortIndex;
this.id = id;
}
}
function push(heap: HeapNode[], node: HeapNode): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
function siftUp(heap: HeapNode[], node: HeapNode, i: number): void {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
return;
}
}
}
function compare(a: HeapNode, b: HeapNode): number {
return a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
}
// 初始堆
const heap: HeapNode[] = [
new HeapNode(2, 0),
new HeapNode(7, 1),
new HeapNode(5, 2),
new HeapNode(12, 3),
new HeapNode(22, 4),
new HeapNode(17, 5),
new HeapNode(25, 6),
];
// 插入新节点
const newNode = new HeapNode(3, 7);
push(heap, newNode);
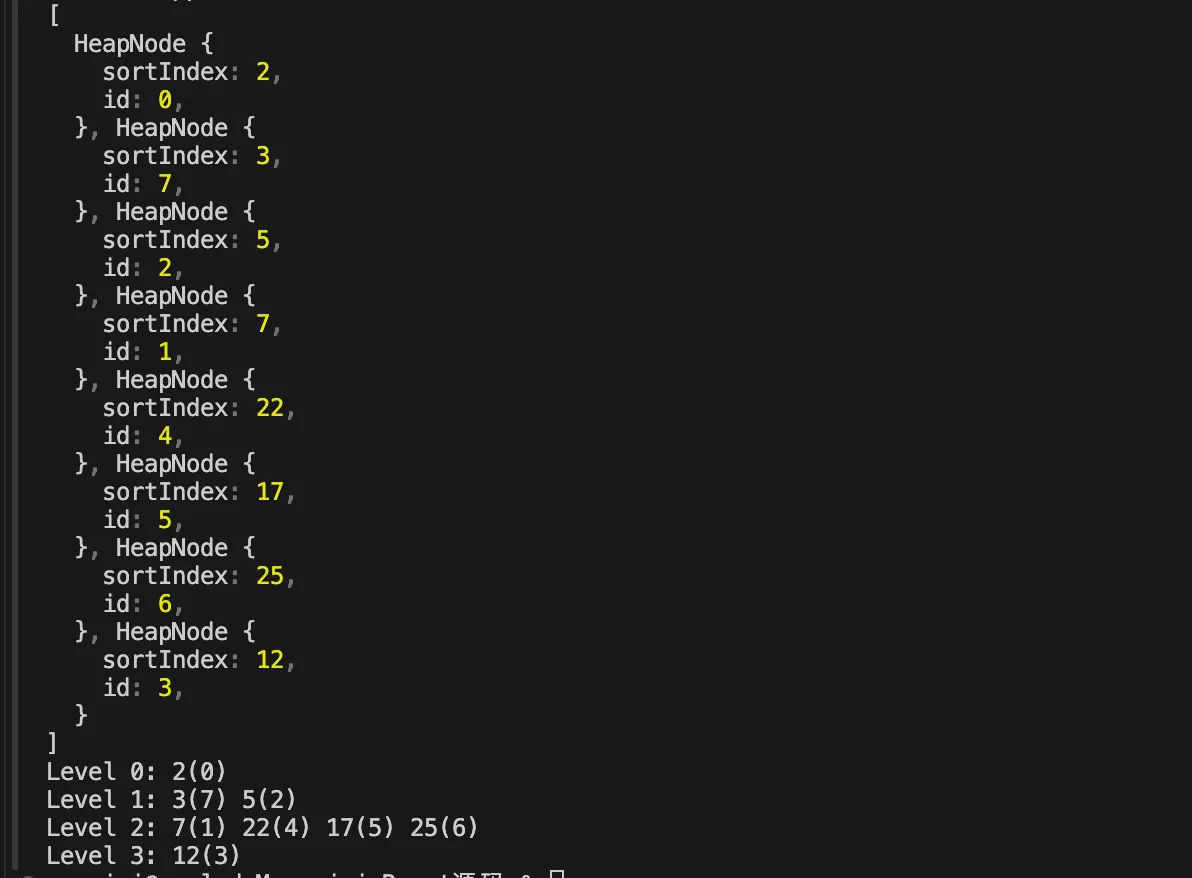
console.log(heap);
function printHeap(heap: HeapNode[]): void {
const levels: string[][] = [];
let level = 0;
let count = 1;
let index = 0;
while (index < heap.length) {
const levelNodes: string[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count && index < heap.length; i++) {
levelNodes.push(`${heap[index].sortIndex}(${heap[index].id})`);
index++;
}
levels.push(levelNodes);
level++;
count *= 2;
}
levels.forEach((levelNodes, i) => {
console.log(`Level ${i}: ${levelNodes.join(' ')}`);
});
}
printHeap(heap);最终输出结果如下图所示:
删除
删除最小堆中的元素,通常是删除堆顶元素,这是最小堆中最小的元素。它是将堆中最后一个元素移动到堆顶的位置,删除完成之后从堆顶开始,将新放置的元素与其子节点进行比较,并下沉到适当的位置,以恢复堆的性质。
假设我们有一个最小堆如下图所示:
5
/ \
8 10
/ \ / \
12 15 20 30现在我们要删除一个堆顶元素,删除完成之后,将堆中的最后一个元素 30 移动到堆顶。
30
/ \
8 10
/ \ / \
12 15 20从堆顶开始,将新放置的元素 30 与其子节点进行比较,并下沉到适当的位置。首先,30 与 8 和 10 比较,8 是最小的,所以交换 30 和 8。然后,继续将 30 与 12 和 15 比较,12 是最小的,所以交换 30 和 12。
8
/ \
12 10
/ \ / \
30 15 20最终的实现代码如下图所示:
class HeapNode {
sortIndex: number;
id: number;
constructor(sortIndex: number, id: number) {
this.sortIndex = sortIndex;
this.id = id;
}
}
function push(heap: HeapNode[], node: HeapNode): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
function siftUp(heap: HeapNode[], node: HeapNode, i: number): void {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
return;
}
}
}
function pop(heap: HeapNode[]): HeapNode | undefined {
if (heap.length === 0) {
return undefined;
}
const first = heap[0];
const last = heap.pop();
if (heap.length > 0 && last !== undefined) {
heap[0] = last;
siftDown(heap, last, 0);
}
return first;
}
function siftDown(heap: HeapNode[], node: HeapNode, i: number): void {
let index = i;
const length = heap.length;
const halfLength = length >>> 1;
while (index < halfLength) {
const leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1;
const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1;
const left = heap[leftIndex];
const right = heap[rightIndex];
let smallest = left;
let smallestIndex = leftIndex;
if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, left) < 0) {
smallest = right;
smallestIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (compare(smallest, node) >= 0) {
break;
}
heap[smallestIndex] = node;
heap[index] = smallest;
index = smallestIndex;
}
}
function compare(a: HeapNode, b: HeapNode): number {
return a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
}
// 初始堆
const heap: HeapNode[] = [
new HeapNode(2, 0),
new HeapNode(7, 1),
new HeapNode(5, 2),
new HeapNode(12, 3),
new HeapNode(22, 4),
new HeapNode(17, 5),
new HeapNode(25, 6),
];
// 插入新节点
const newNode = new HeapNode(3, 7);
push(heap, newNode);
console.log('Heap after push:');
printHeap(heap);
// 弹出堆顶节点
const poppedNode = pop(heap);
console.log(
`Popped node: ${poppedNode ? `${poppedNode.sortIndex}(${poppedNode.id})` : 'undefined'}`,
);
console.log('Heap after pop:');
printHeap(heap);
function printHeap(heap: HeapNode[]): void {
const levels: string[][] = [];
let level = 0;
let count = 1;
let index = 0;
while (index < heap.length) {
const levelNodes: string[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count && index < heap.length; i++) {
levelNodes.push(`${heap[index].sortIndex}(${heap[index].id})`);
index++;
}
levels.push(levelNodes);
level++;
count *= 2;
}
levels.forEach((levelNodes, i) => {
console.log(`Level ${i}: ${levelNodes.join(' ')}`);
});
}最终输出结果如下图所示:

在上面的代码中,siftDown 函数用于在删除堆顶元素后,从新的堆顶位置向下调整堆的性质。它比较当前节点与其子节点,如果当前节点大于子节点中的较小者,则交换它们的位置,直到找到合适的位置或者到达堆的底部。
最终完整的 React 源码实现如下代码:
// src/react/packages/scheduler/src/SchedulerMinHeap.js
type Heap = Array<Node>;
type Node = {|
id: number,
sortIndex: number,
|};
export function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
export function peek(heap: Heap): Node | null {
return heap.length === 0 ? null : heap[0];
}
export function pop(heap: Heap): Node | null {
if (heap.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const first = heap[0];
const last = heap.pop();
if (last !== first) {
heap[0] = last;
siftDown(heap, last, 0);
}
return first;
}
function siftUp(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
// The parent is larger. Swap positions.
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
// The parent is smaller. Exit.
return;
}
}
}
function siftDown(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
const length = heap.length;
const halfLength = length >>> 1;
while (index < halfLength) {
const leftIndex = (index + 1) * 2 - 1;
const left = heap[leftIndex];
const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1;
const right = heap[rightIndex];
// If the left or right node is smaller, swap with the smaller of those.
if (compare(left, node) < 0) {
if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, left) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
heap[index] = left;
heap[leftIndex] = node;
index = leftIndex;
}
} else if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, node) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
// Neither child is smaller. Exit.
return;
}
}
}
function compare(a, b) {
// Compare sort index first, then task id.
const diff = a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
return diff !== 0 ? diff : a.id - b.id;
}参考资料
总结
React 使用最小堆来高效管理任务优先级,确保高优先级任务能被快速处理,从而提高应用的性能和响应速度。这使得用户界面在高负载下仍然能够流畅运行。